Credit: www.usbank.com
Understanding Inflation
Inflation means prices of goods and services go up. It is a natural part of the economy. When inflation is high, money loses value. You need more money to buy the same things.
Central banks, like the Federal Reserve in the U.S., watch inflation closely. They try to keep it at a safe level. Too much inflation is bad. But too little inflation is also bad. Balance is key.
Why Does Inflation Happen?
Inflation can happen for many reasons. Here are a few:
- More money in the economy.
- Higher demand for goods and services.
- Higher costs for businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/realinterestrate.asp-final-9a1778bfb52748c798d30b2e2411f446.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Loan Interest Rates
When you borrow money, you pay interest. The interest rate is the cost of borrowing. It is a percentage of the loan amount. Banks and lenders set interest rates. But many factors influence these rates.
Factors Affecting Interest Rates
Several factors affect interest rates:
- Inflation rates.
- Economic growth.
- Central bank policies.
- Credit risk.
How Inflation Affects Loan Interest Rates
Inflation has a direct impact on loan interest rates. Here’s how:
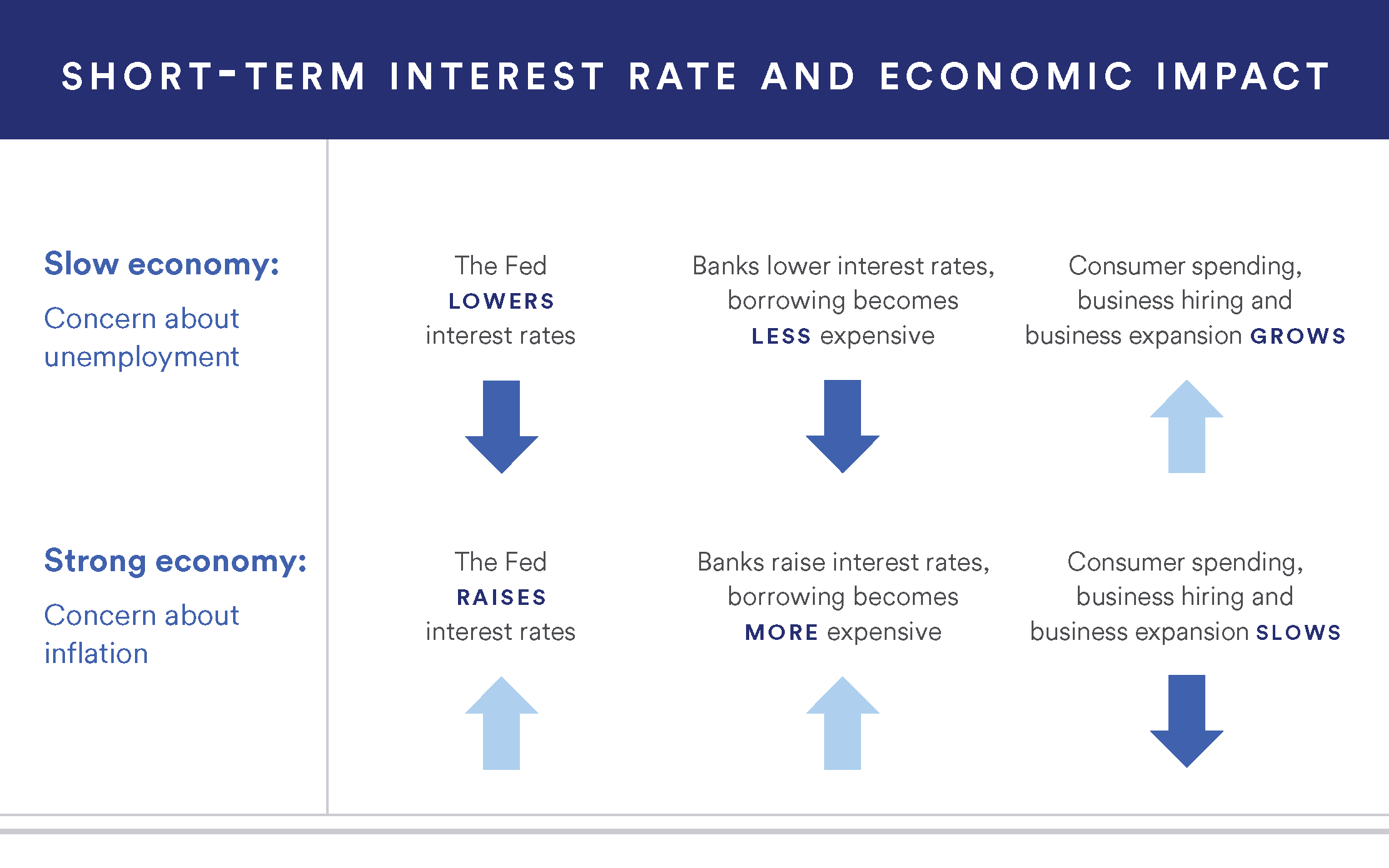
1. Higher Inflation Leads To Higher Interest Rates
When inflation is high, lenders charge higher interest rates. They want to make sure they earn money even as prices rise. High inflation means the value of money falls. So, lenders need to protect their earnings.
2. Central Bank Actions
Central banks may raise their rates to control inflation. When central banks raise rates, other banks follow. This means higher loan interest rates for everyone.
3. Reduced Borrowing
High interest rates mean loans cost more. People and businesses borrow less. This can slow down the economy. But it can also help control inflation.
4. Inflation Expectations
If people expect inflation to rise, lenders will raise rates. They want to stay ahead of inflation. Future inflation expectations can affect current rates.
Impact on Different Types of Loans
Different loans are affected in different ways. Let’s look at some common types of loans.
1. Home Loans
Home loans are often long-term. High inflation can lead to higher home loan rates. This makes buying a home more expensive. Monthly payments go up. It can also affect the housing market. Fewer people can afford to buy homes.
2. Personal Loans
Personal loans are usually short-term. High inflation can make these loans more expensive too. Interest rates go up. Monthly payments increase. It becomes harder to pay off the loan quickly.
3. Business Loans
Businesses need loans to grow. High inflation can hurt business borrowing. Higher interest rates mean higher costs. This can slow down business growth. It can also lead to higher prices for consumers.
4. Student Loans
Student loans are often long-term. High inflation can increase interest rates on these loans. This means students pay more over time. Education becomes more expensive.
How to Manage Loans During Inflation
Managing loans during inflation can be tough. But there are ways to handle it. Here are some tips:
1. Lock In Fixed Rates
If you can, choose fixed-rate loans. Fixed rates do not change. Even if inflation goes up, your rate stays the same. This can save you money in the long run.
2. Pay Off High-interest Debt
Focus on paying off loans with high interest. This can reduce your monthly payments. It can also save you money in the long run.
3. Refinance Loans
If rates go down, consider refinancing. This means getting a new loan at a lower rate. It can reduce your monthly payments. It can also save you money over time.
4. Budget Wisely
Make a budget and stick to it. Know your income and expenses. Cut down on unnecessary spending. This can help you manage your loans better.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Inflation?
Inflation is the rise in the prices of goods and services over time.
How Does Inflation Affect Loans?
Inflation often leads to higher interest rates on loans, making borrowing more expensive.
Why Do Interest Rates Increase With Inflation?
Lenders raise interest rates to maintain their profit margins when inflation reduces the value of money.
Can Inflation Decrease Interest Rates?
Rarely. Central banks might lower rates during economic downturns, but generally, inflation increases rates.
Conclusion
Inflation affects loan interest rates in many ways. High inflation leads to higher rates. This makes borrowing more expensive. Different loans are affected differently. But there are ways to manage loans during inflation. Choose fixed rates, pay off high-interest debt, refinance if possible, and budget wisely.
Understanding inflation and its impact on loans is important. It helps you make better financial decisions. Stay informed and plan ahead. This way, you can handle the challenges of inflation better.
